Sensitive MRD testing in DLBCL can be more prognostic of outcomes than imaging alone
Incorporate NGS MRD into your clinical trials to get an early read on efficacy
While important tools in detecting and monitoring diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the qualitative nature of imaging tests can lead to difficulties in understanding the true magnitude of changes in disease burden. When conducting DLBCL clinical trials, NGS MRD is an additional objective measure of efficacy to complement imaging, which helps ensure you are getting the best data to progress your clinical trial.
Predictive of outcomes
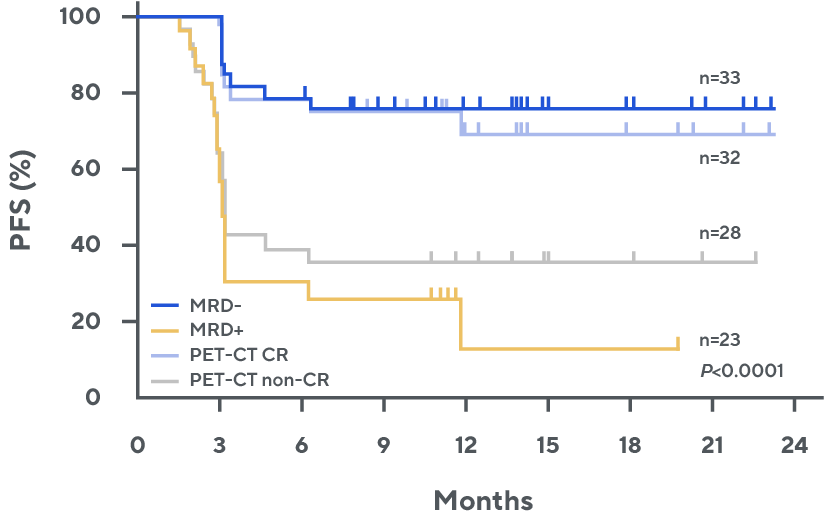
MRD status post-CAR T was more predictive of outcomes in patients with equivocal imaging.
Progression-free survival by day 28 MRD or PET-CT*, 1
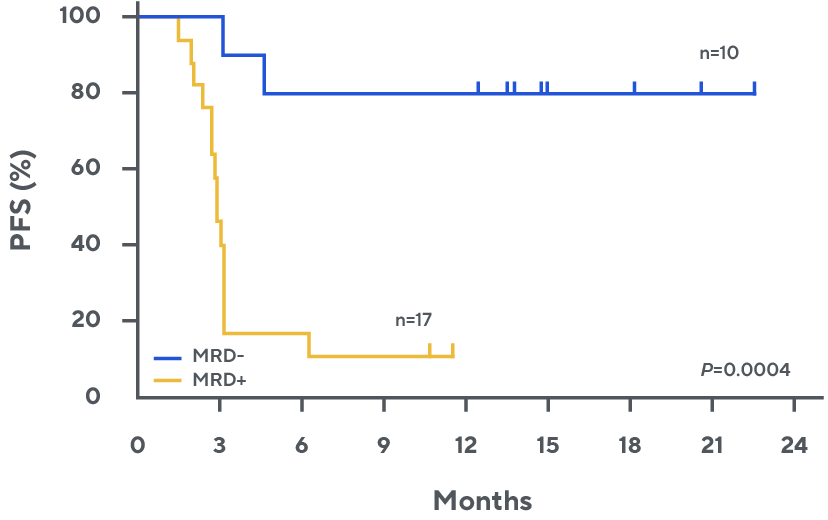
Progression-free survival by day 28 MRD for patients with partial response or stable disease by PET-CT*, †, ‡, 1
A strong indicator of prognosis
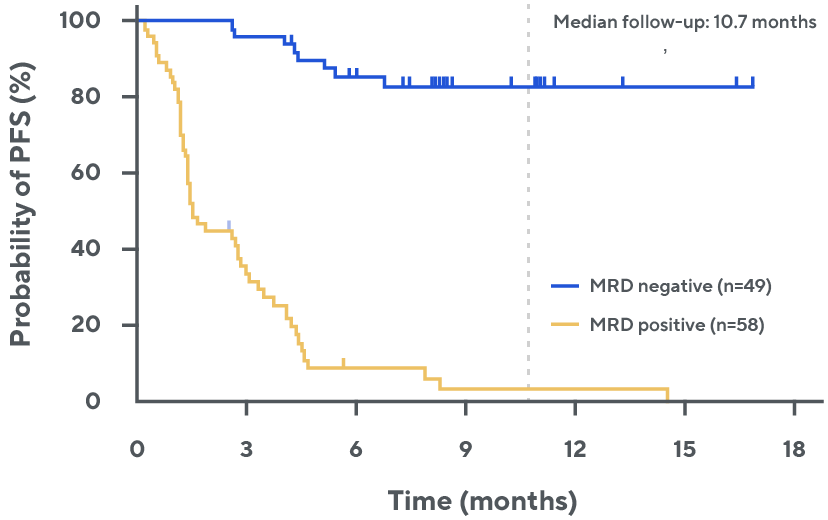
MRD negativity was associated with duration of response in patients with relapsing/refractory DLBCL treated with epcoritamab in EPCORE NHL-1.
Progression-free survival by MRD status among all evaluable patients§, ¶, 2
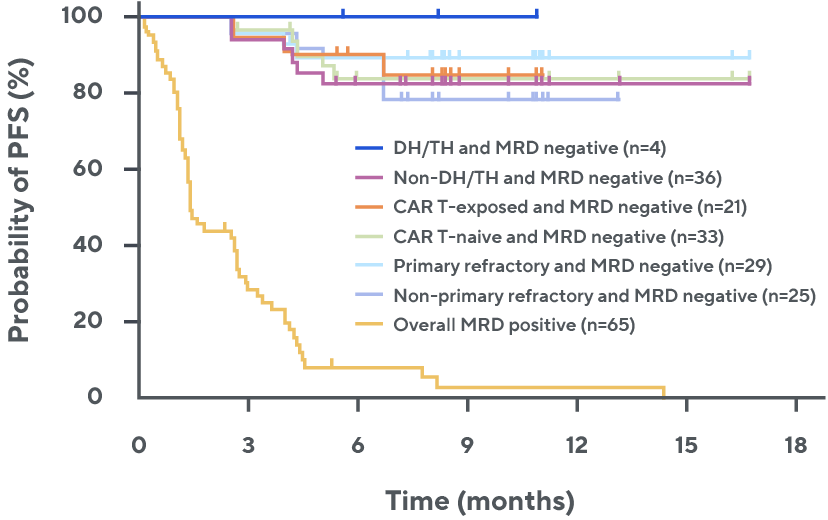
Progression-free survival by MRD status across subgroups§, ¶, 3
Extensive analytical validation of NGS MRD
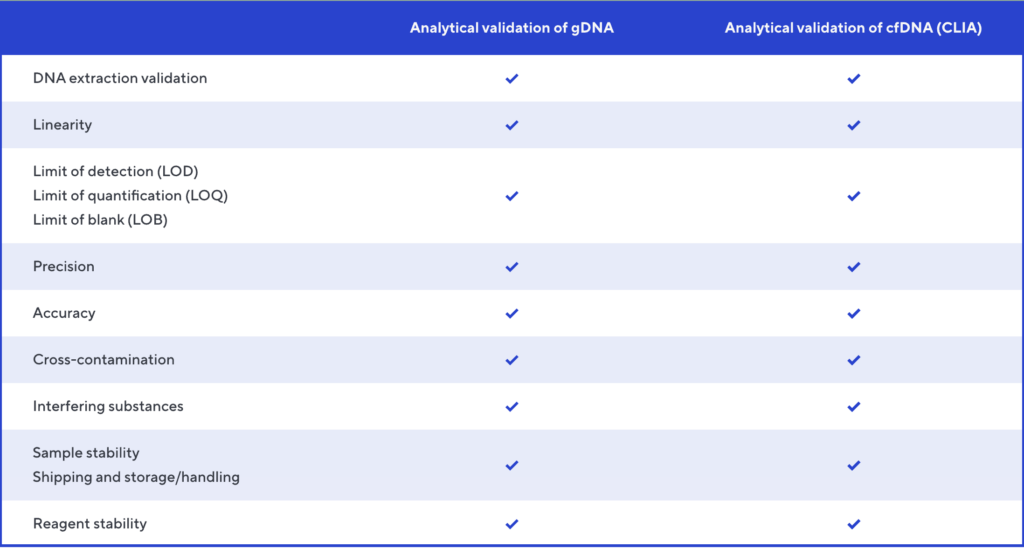
Improved assay performance
- Adaptive NGS MRD was recently updated to improve the sensitivity of the existing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) assay.
- This update includes a new extraction method, which is available for GCP-compliant use in research and clinical trials for MRD detection in DLBCL. It enables extraction of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from up to 10 mL of plasma, resulting in a higher yield of cfDNA.
- While sensitivity increases, there is no impact on limit of detection or limit of blank (1.9 and 0 clonal molecules, respectively).
Widely used in the clinic and in biopharma trials
- clonoSEQ, the NGS MRD clinical analog, is used by thousands of physicians to track minimal residual disease (MRD), which has informed treatment decisions for more than 40,000 patients across hematologic malignancies.#
- clonoSEQ is FDA cleared in three hematology-oncology indications and CLIA-validated in four indications.#
- clonoSEQ is used at all 33 National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) sites.
- NGS MRD is used by more than 40 biopharma partners and in more than 160 active industry-sponsored clinical trials.
- NGS MRD and clonoSEQ have been included in more than 150 publications.
Contact bd@adaptivebiotech.com to learn more.
* MRD was evaluated via NGS MRD assay to assess for ctDNA in plasma. Any detectable ctDNA was considered MRD positive.
† PR or SD. PR: n=24; SD: n=4.
‡ One MRD-negative patient died due to treatment-related Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia at 4.5 months.
§ NGS-MRD of ctDNA.
¶ Median follow-up was 10.7 months. ctDNA: circulating tumor DNA; DH/TH, double-hit/triple-hit.
# clonoSEQ is FDA cleared for MRD testing in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in bone marrow, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in bone marrow and blood, and multiple myeloma (MM) in bone marrow. It is CLIA validated as a lab developed test (LDT) in MM using blood; ALL using blood; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) using blood in EDTA tubes and cfDNA in plasma; T-cell lymphoma (TCL) in bone marrow and blood.
1. Frank MJ et al., J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jun 16;JCO2100377.
2. Thieblemont C et al., EHA 2022. Abstract LB2364.
3. Phillips T et al., ASH 2022. Abstract 4251.